Cardiac CT scan
A CT scan (or CAT scan) of the heart can assess for disease in the coronary arteries, which supply the heart muscle with blood, and can also identify problems with the heart’s structure and function. It often provides just as much information as an invasive catheterization.
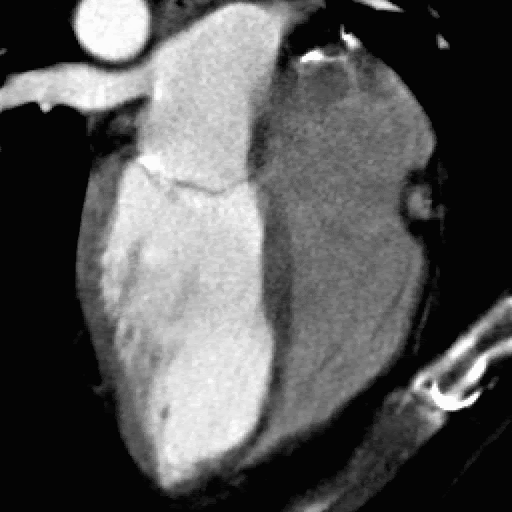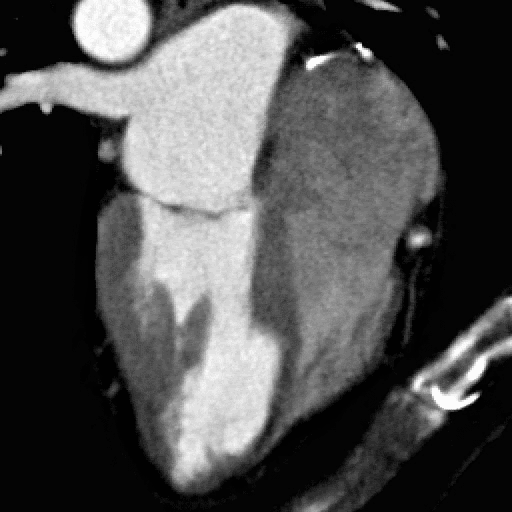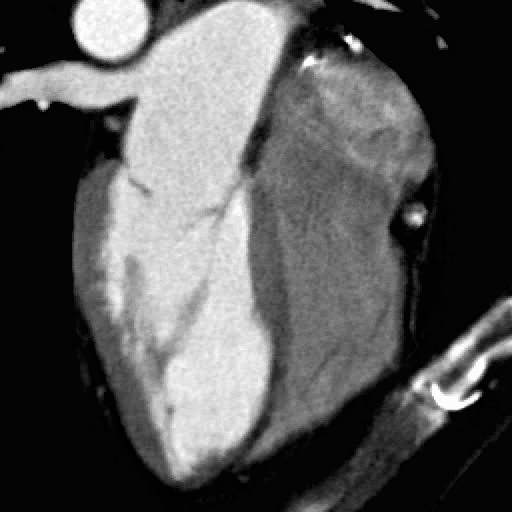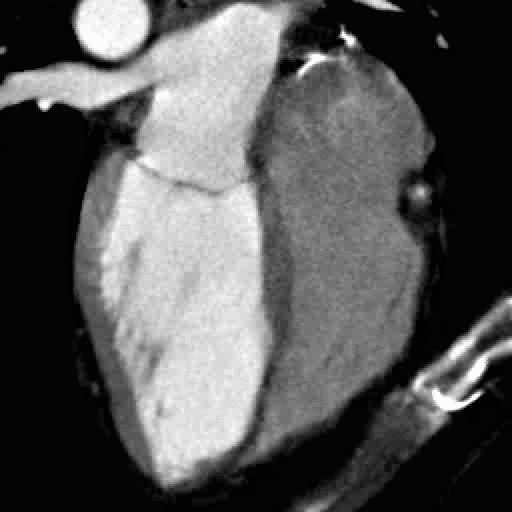
What You Need to Know Before Your Cardiac CT scan
To ensure the best experience possible, please note the following important points:
Have an empty stomach
Do not eat or drink anything other than water for at least four hours prior to your test.
If you have a history of allergies or reactions to contrast, let us know in advance.
If you have a history of a contrast reaction, we’ll need to administer steroids prior to your scan to reduce the risk of it happening again. If your reaction was really severe, we may have to cancel the scan altogether.
If you are pregnant, please let us know before your scan.
We do not prescribe CT scans to women who are pregnant, since there is unacceptable radiation risk to the fetus. If you have become pregnant since the scan was ordered, please let us know and we will find an alternative test.
More Details
What is a cardiac CT scan?
A CT scan (or CAT) scan is a test in which energy beams are transmitted through the body. Different tissues absorb the energy to a different extent, which allows us to reconstruct a picture of the inside of your body. By timing the energy beams to the heartbeat, we can obtain a clear view of the heart both at rest and in motion.
What is a calcium score?
A calcium score is a CT scan of the heart that assesses the presence and burden of calcium in the arteries of the heart. In this location, calcium is a surrogate marker of plaque. The more calcium, the more plaque.
Intravenous contrast is not required to visualize calcium, so you will not need an IV for this test.
We typically perform a calcium score when your overall risk of heart disease is intermediate, and we want more information before deciding how aggressively to control your cholesterol and blood pressure. A high calcium score is a risk marker that signals we need to better control other risk factors.
What is a coronary CT angiogram?
A coronary CT angiogram (CCTA) is a CT scan of the heart that directly visualizes the coronary arteries. Before the scan, we administer intravenous contrast, which fills and highlights the coronary arteries. In this way, we can directly visualize plaque in those arteries, without relying on surrogate markers such as calcium.
We typically order CCTAs when a patient has an abnormal or equivocal stress test, in order to more accurately define the presence and burden of coronary artery disease. If a blockage is found, we use a technology known as CT-FFR to better determine if it needs treatment.
When will I get my results?
The results of a transthoracic or stress echocardiogram will be provided via telephone or MyChart within a few days of your test. The results of a transesophageal echocardiogram will be provided immediately after the test.
Is a CT scan safe?
Yes, a CT scan is a common and safe test, though there are two main risks.
First, there is a small amount of radiation associated with this test. We take great care to minimize the radiation dose, but a small dose is unavoidable. The long-term risk of health complications related to a single radiation exposure is low; however, repeated exposures (from multiple scans) result in greater risk.
Second, there is some risk associated with intravenous contrast. First, some people have allergic reactions to contrast. If you have a known history of allergic reactions, we will provide medications before your scan to reduce this risk. In addition, intravenous contrast may cause kidney dysfunction, especially among those with baseline kidney disease. We will check your kidney function before the test and only proceed if the risk is low.

